-
Chapter 19: Relationships of organisms with one another and with the environment
Energy Flow: 1. Principal Source of Energy: 2. Dependence on Photosynthesis: 3. Flow of Energy Through Food Chains and Webs: 4. Construction and Interpretation of Food Chains: 5. Terminology: 6. Food Webs: 7. Inefficiency in Energy Transfer: 8. Limited Trophic Levels: 9. Energy Efficiency in Human Diet: 10. Pyramids: Understanding energy flow in ecosystems, from […]
-
Chapter 18: Biotechnology and Genetic Modification
1. Role of Yeast 2. Bacteria in Biotechnology 3. Why Bacteria in Biotechnology 4. Fermenters in Large-Scale Production 5. Enzymes in Various Applications Understanding the applications of biotechnology and genetic modification involving yeast, bacteria, and enzymes highlights their diverse roles in industries and everyday products. Genetic Modification: 1. Definition of Genetic Modification: 2. Insertion of […]
-
Chapter 17: Inheritance – Variation
1. Description of Variation: 2. Continuous Variation: 3. Discontinuous Variation: 4. Causes of Variation: 5. Examples of Continuous and Discontinuous Variation: Understanding the nature of variation, whether continuous or discontinuous, provides insights into the underlying genetic and environmental factors shaping the diversity observed within a species. DNA Structure and Function: 1. Structure of a DNA […]
-
Chapter 14: Coordination and Control
Role of the Nervous System: The nervous system, comprising the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, coordinates and regulates body functions. Mammalian Nervous System Components: (a) Central Nervous System (CNS): Consists of the brain and spinal cord. (b) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-the-Nervous-System.aspx Electrical impulses travel along neurons, […]
-
Chapter 12: Disease and Immunity
Definition: A pathogen is a microscopic organism, such as a virus, bacterium, fungus, or parasite, capable of causing disease in its host. Transmissible Disease: Transmissible diseases are those that can spread from one individual to another. Common modes of transmission include direct contact, airborne particles, contaminated surfaces, and vectors like mosquitoes. Pathogen Transmission: (a) Direct […]
-
Chapter 13: Excretion
Embarking on the exploration of excretion unveils the intricate mechanisms by which organisms rid themselves of toxins and metabolic byproducts. Excretion, a fundamental process in biology, ensures the body maintains internal balance by eliminating harmful substances like urea and carbon dioxide. From the kidneys’ meticulous filtration to the liver’s pivotal role in amino acid metabolism, […]
-
Chapter 10 – Respiration
Embarking on the journey through the intricacies of respiration, one delves into the fundamental biochemical processes underpinning life itself. At its core, respiration orchestrates a symphony of reactions within the mitochondria of cells, transforming glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water. This cellular ballet, often termed aerobic respiration, fuels the myriad activities sustaining […]
-
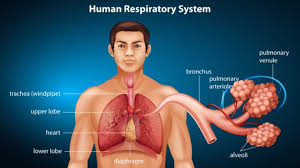
Chapter 9: Human Gas Exchange

1. Features of Gas Exchange Surfaces: 2. Percentages of Gases in Atmospheric Air: 3. Inspired and Expired Air Differences: 4. Identification of Respiratory System Components: 5. Characteristics and Role of Alveoli in Gas Exchange: 6. Identification of Thoracic Components: 7. Role in Breathing (Volume and Pressure Changes): 8. Effect of Physical Activity on Breathing: 9. […]